Mapwork Skills Notes for Geography Grade 12 Mapwork skills are essential in geography, and they often include a range of tasks such as reading and interpreting maps, using map symbols, understanding scale and distance, and analyzing spatial patterns.
Here are some key mapwork skills notes for Geography Grade 12:
- Map Reading:
- Understand the key components of a map, such as title, legend, scale, and compass rose.
- Read and interpret different types of maps, including topographic maps, political maps, and thematic maps.
- Map Symbols:
- Familiarize yourself with common map symbols and their meanings. These symbols represent physical features, cultural features, and other elements on the map.
- Scale and Distance:
- Understand the concept of scale on a map and how it relates to distance on the ground.
- Differentiate between large-scale and small-scale maps and their uses.
- Direction and Orientation:
- Use a compass rose to determine cardinal directions (north, south, east, west) and intermediate directions.
- Understand how to orient yourself on a map using a compass or other directional indicators.
- Grid Systems:
- Learn how to use grid systems on maps to locate specific points and determine coordinates.
- Understand latitude and longitude and their significance in locating places on the Earth’s surface.
- Topographic Maps:
- Interpret contour lines on topographic maps to understand the relief and elevation of the land.
- Recognize landforms, valleys, hills, and other physical features on a topographic map.
- Spatial Patterns:
- Analyze spatial patterns and distribution of features on a map.
- Understand the factors influencing the distribution of human and physical features.
- Map Skills in Data Analysis:
- Use maps to analyze and interpret data related to population, climate, land use, and other geographical phenomena.
- Understand how to extract information from thematic maps and use it for analysis.
- Map Sketching:
- Develop the skill of sketching maps, indicating key features, and adding annotations.
- Pay attention to accuracy in proportions and placement of features.
- Map Interpretation:
- Develop critical thinking skills to interpret maps in the context of geographical processes and trends.
- Relate information from maps to broader geographical concepts and theories.
Let’s understand what Maps are
Maps show what the world looks like from above. They are very useful because they give information and show where places are. There are many different types of maps. These include street maps, road maps, atlases and ordnance survey (OS) maps.
Map Techniques you should know
- A map is a reduced representation of reality.
- Maps are either drawn on paper or produced digitally.
- Maps show reality in two dimensions. If we want to represent the third dimension (height or altitude) we have to use contour lines or spot heights.
- On many maps (including synoptic maps) it is not necessary to show altitude. However, symbols are needed to represent other information on the map.
How to Interpret weather and climate-related data in Geography studies?
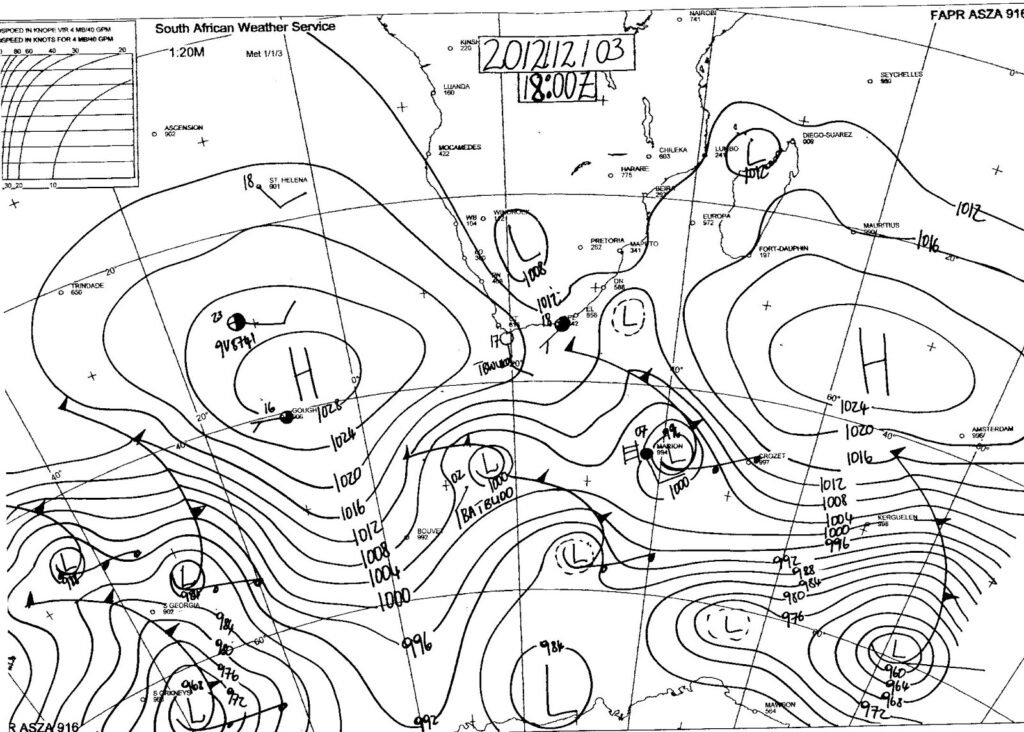
- A synoptic weather map provides a summary of weather conditions over a particular area at a particular time.
- Synoptic charts, satellite images and other data give us valuable information about the weather and climate.
- To make a weather forecast, forecasters examine a series of synoptic charts and compare them to satellite images and data from weather stations and weather balloons.
- Synoptic charts show weather-related data only and include isobars, station models (the symbols that show a variety of conditions) and weather features.
- Satellite images are remotely sensed. This means that there is no contact between the sensor in the satellite and the item being sensed (e.g. the Earth’s surface).
- Satellite images are digital images captured by sensors in satellites that orbit the Earth.
- Meteosat satellites are weather satellites and their sensors capture images of large areas.
- Satellite sensors don’t just capture images; data is also collected from outside the visible light spectrum, for instance, infrared.
Map and photo interpretation: reading and analysing features
- In settlement geography, map and photo interpretation is just as important as in physical geography.
- Settlements are often influenced by physical features (slope steepness, soil, availability of water, avoidance of marshy areas and wetlands), so you must be able to read and analyse physical features in the landscape.
- Constructed features are those things which humans place (build) on the landscape to serve their needs.
- Communications and transport (telephone lines, roads, railways), power lines, dams, and the settlements themselves are examples of constructed features.